# 欠拟合与过拟合任务
欠拟合:模型太简单了无法拟合训练集 过拟合:模型太复杂了,为了满足少数数据反而使验证集越来越远
# 加载带有噪音的二分类数据集
data.js
export function getData(numSamples, variance) {
let points = [];
function genGauss(cx, cy, label) {
for (let i = 0; i < numSamples / 2; i++) {
let x = normalRandom(cx, variance);
let y = normalRandom(cy, variance);
points.push({ x, y, label });
}
}
genGauss(2, 2, 1);
genGauss(-2, -2, 0);
return points;
}
/**
* Samples from a normal distribution. Uses the seedrandom library as the
* random generator.
*
* @param mean The mean. Default is 0.
* @param variance The variance. Default is 1.
*/
function normalRandom(mean = 0, variance = 1) {
let v1, v2, s;
do {
v1 = 2 * Math.random() - 1;
v2 = 2 * Math.random() - 1;
s = v1 * v1 + v2 * v2;
} while (s > 1);
let result = Math.sqrt((-2 * Math.log(s)) / s) * v1;
return mean + Math.sqrt(variance) * result;
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
import * as tfvis from "@tensorflow/tfjs-vis";
import { getData } from "./data";
window.onload = () => {
// 第二个参数是方差,值越大噪声越大
const data = getData(200, 3);
tfvis.render.scatterplot(
{ name: "训练数据" },
{
values: [data.filter(p => p.label === 1), data.filter(p => p.label === 0)]
}
);
};
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
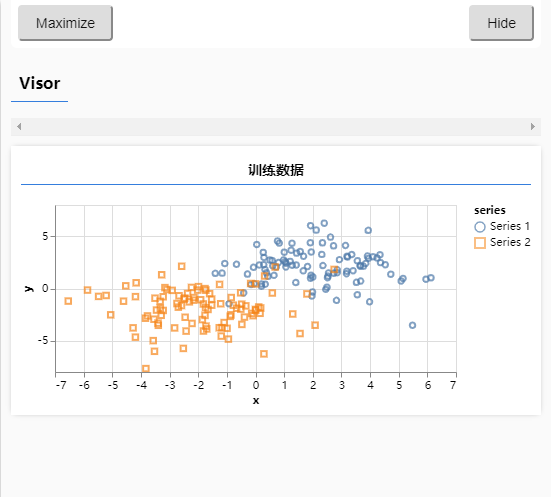
# 使用简单神经网络模拟欠拟合
引用 xor 的数据集,使用简单的二分模型来训练
import * as tfvis from "@tensorflow/tfjs-vis";
import * as tf from "@tensorflow/tfjs";
import { getData } from "../xor/data";
window.onload = async () => {
const data = getData(200);
tfvis.render.scatterplot(
{ name: "训练数据" },
{
values: [data.filter(p => p.label === 1), data.filter(p => p.label === 0)]
}
);
const model = tf.sequential();
model.add(
tf.layers.dense({
units: 1,
activation: "sigmoid",
inputShape: [2]
})
);
model.compile({
loss: tf.losses.logLoss,
optimizer: tf.train.adam(0.1)
});
const inputs = tf.tensor(data.map(p => [p.x, p.y]));
const labels = tf.tensor(data.map(p => [p.label]));
await model.fit(inputs, labels, {
validationSplit: 0.2,
epochs: 200,
callbacks: tfvis.show.fitCallbacks(
{ name: "训练效果" },
["loss", "val_loss"],
{ callbacks: ["onEpochEnd"] }
)
});
};
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
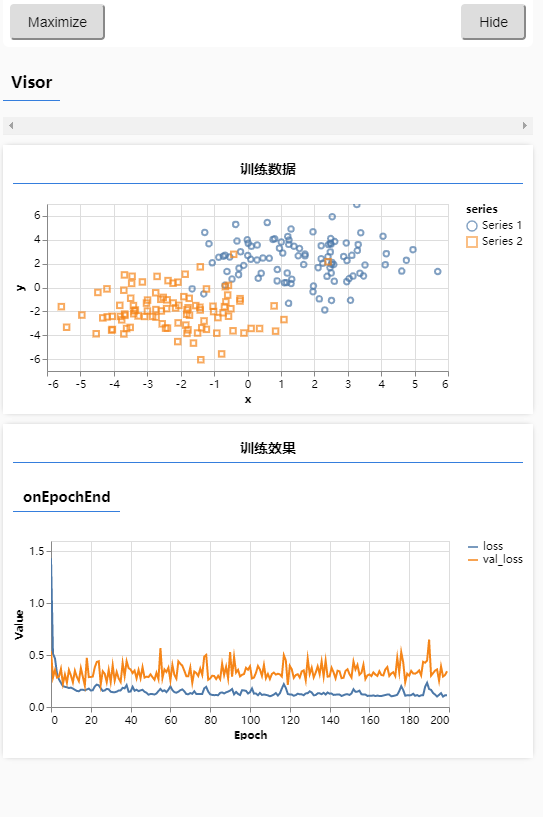
- 从结果上看,训练集到 0.5 就下不去了,而验证集则更是一路飘飞
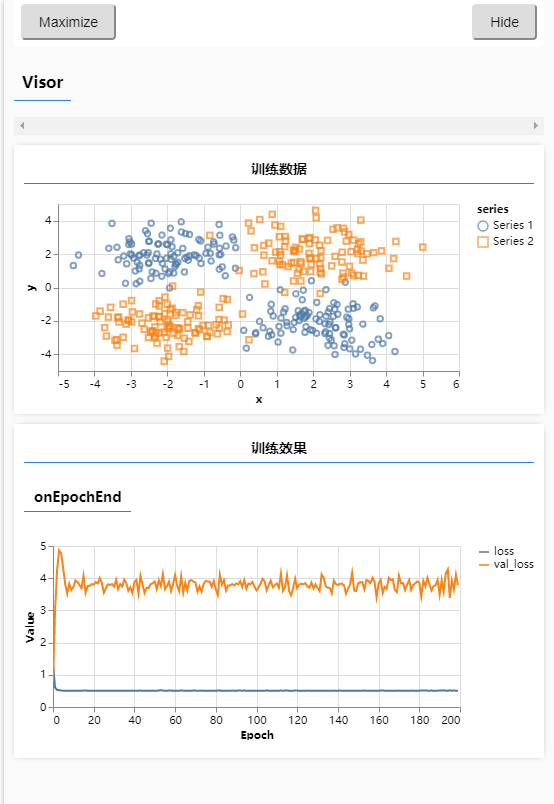
# 使用复杂神经网络演示过拟合
import * as tfvis from "@tensorflow/tfjs-vis";
import * as tf from "@tensorflow/tfjs";
import { getData } from "./data";
window.onload = async () => {
const data = getData(200, 3);
tfvis.render.scatterplot(
{ name: "训练数据" },
{
values: [data.filter(p => p.label === 1), data.filter(p => p.label === 0)]
}
);
const model = tf.sequential();
model.add(
tf.layers.dense({
units: 10,
inputShape: [2],
activation: "tanh"
})
);
model.add(
tf.layers.dense({
units: 1,
activation: "sigmoid"
})
);
model.compile({
loss: tf.losses.logLoss,
optimizer: tf.train.adam(0.1)
});
const inputs = tf.tensor(data.map(p => [p.x, p.y]));
const labels = tf.tensor(data.map(p => [p.label]));
await model.fit(inputs, labels, {
validationSplit: 0.2,
epochs: 200,
callbacks: tfvis.show.fitCallbacks(
{ name: "训练效果" },
["loss", "val_loss"],
{ callbacks: ["onEpochEnd"] }
)
});
};
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
- 由图可以看到,虽然训练集的损失降了下来,但是验证集飘飞
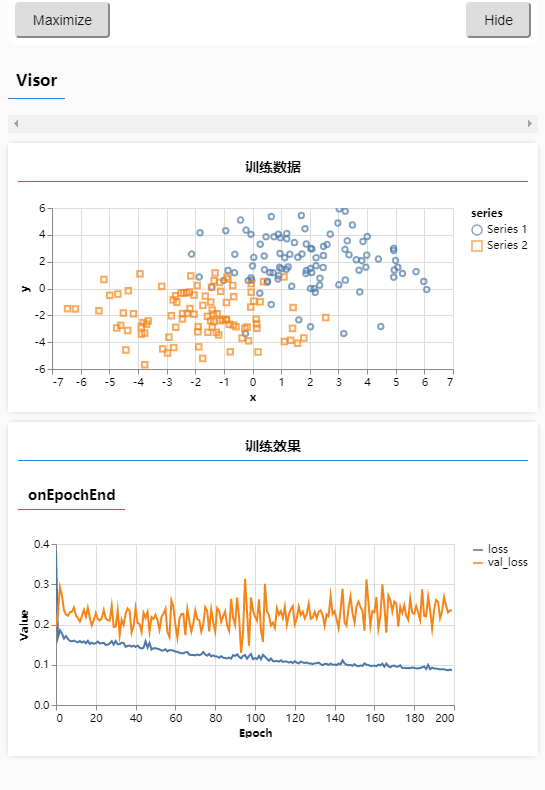
# 过拟合应对法:早定法、权重衰减、丢弃法
import * as tfvis from '@tensorflow/tfjs-vis';
import * as tf from '@tensorflow/tfjs'
import { getData } from './data';
window.onload = async () => {
const data = getData(200, 3);
tfvis.render.scatterplot(
{ name: '训练数据' },
{
values: [
data.filter(p => p.label === 1),
data.filter(p => p.label === 0)
]
}
)
const model = tf.sequential();
model.add(tf.layers.dense({
units: 10,
inputShape: [2],
activation: 'tanh',
//---------------------------权重衰减--------------------------------
// 设置正则化,把负责的模型权重衰减掉
// kernelRegularizer: tf.regularizers.l2({l2: 1}),
//-----------------------------------------------------------
}))
// --------------------------丢弃法---------------------------------------
// 在复杂的层下面加一个丢弃层,参数是丢弃率,将复杂的神经元丢掉一部分使他变简单
model.add(tf.layers.dropout({rate: 0.9}))
// -----------------------------------------------------------------
model.add(tf.layers.dense({
units: 1,
activation: 'sigmoid',
}))
model.compile({
loss: tf.losses.logLoss,
optimizer: tf.train.adam(0.1)
})
const inputs = tf.tensor(data.map(p => [p.x, p.y]));
const labels = tf.tensor(data.map(p => [p.label]));
await model.fit(inputs, labels, {
validationSplit: 0.2,
epochs: 200,
callbacks: tfvis.show.fitCallbacks(
{ name: '训练效果' },
['loss', 'val_loss'],
{ callbacks: ['onEpochEnd'] }
)
})
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
可以看到通过减小模型复杂度将过拟合减小