# React 源码解读(六) hooks 原理(useState)
# useState 原理
首先找到入口 ReactHooks.js 找到 useState 方法
ReactHooks.js
export function useState<S>(initialState: (() => S) | S) {
const dispatcher = resolveDispatcher();
return dispatcher.useState(initialState);
}
1
2
3
4
2
3
4
- 可以看到只有这么两行,跟随到
resolveDispatcher()方法中去看到这样一句const dispatcher = ReactCurrentDispatcher.current; - 继续找到
ReactCurrentDispatcher
ReactCurrentDispatcher.js
const ReactCurrentDispatcher = {
/**
* @internal
* @type {ReactComponent}
*/
current: (null: null | Dispatcher)
};
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
2
3
4
5
6
7
- 可以看到此时的
ReactCurrentDispatcher是空的,但是这部分会在代码调试的过程中进行赋值
ReactFiberScheduler.js
function renderRoot(root: FiberRoot, isYieldy: boolean): void {
//...
isWorking = true;
// 设置 ReactCurrentDispatcher, 包含所有hooks的实现
const previousDispatcher = ReactCurrentDispatcher.current;
ReactCurrentDispatcher.current = ContextOnlyDispatcher;
//...
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
- 可以看出 hooks 也是深入的参与了整个的生命周期
- 为什么不在一开始就赋值而是在后面实时的赋值
- 因为 hooks 只能在 function 中使用,通过多次检测就可以判断是否能够使用
- ReactCurrentDispatcher.current 在执行的时候包含所有的 hooks 的实现
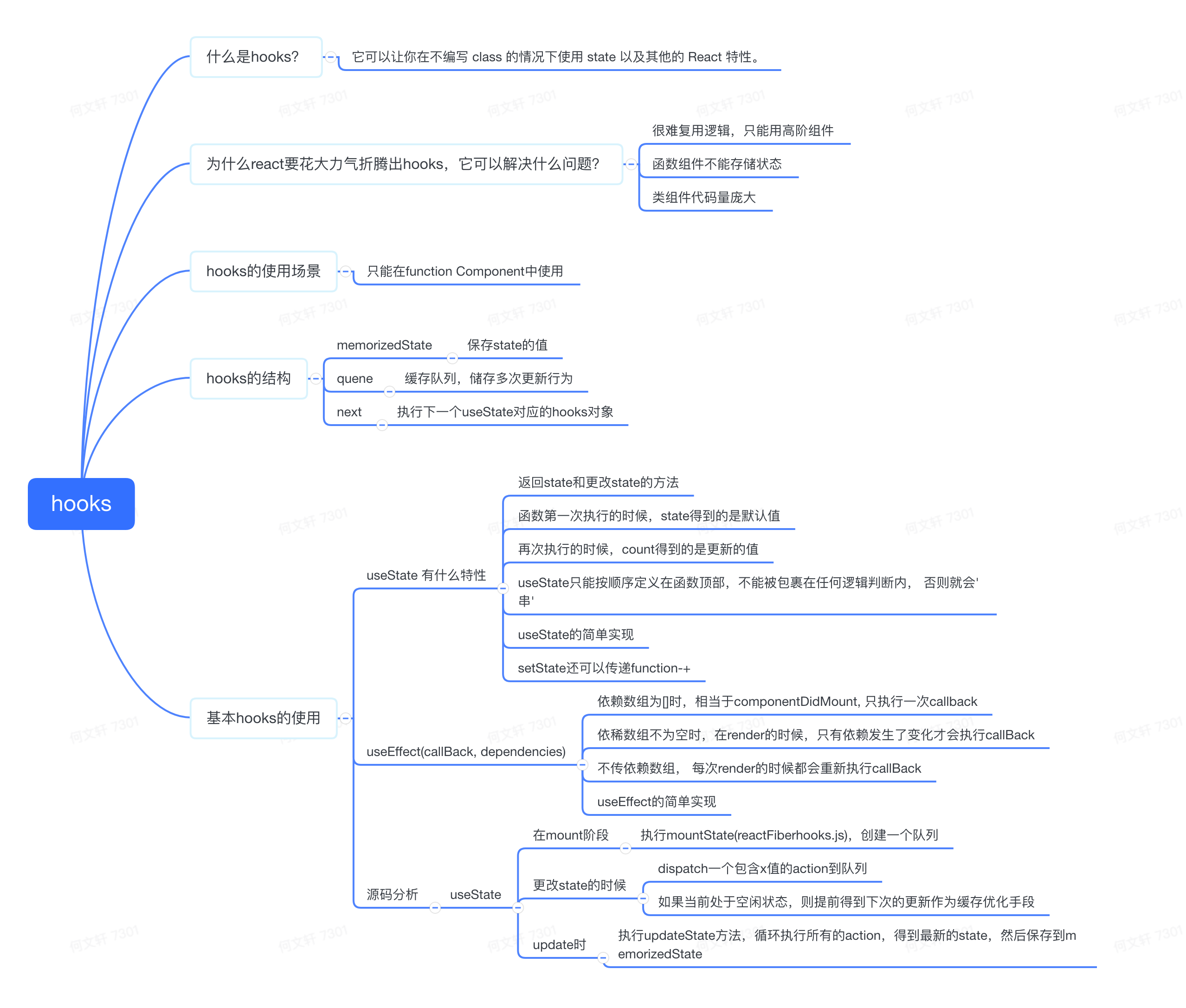
useState 分为三个阶段
- 初始化阶段(在 mount 阶段)
- 执行
mountState(reactFiberhooks.js),创建一个队列
- 执行
- 更改
state的时候dispatch一个包含 x 值的action到队列- 如果当前处于空闲状态,则提前得到下次的更新作为缓存优化手段
- 更新阶段
update时- 执行
updateState方法,循环执行所有的action,得到最新的state,然后保存到memorizedState
- 执行
# 如何区分是处于哪个阶段
ReactFiberHooks.js 中找到 renderWithHooks 方法,有这样一段关键部分
ReactFiberHooks.js
// 区分是Mount还是Update
ReactCurrentDispatcher.current =
nextCurrentHook === null ? HooksDispatcherOnMount : HooksDispatcherOnUpdate;
1
2
3
2
3
- 判断
nextCurrentHook是否为空,空的话就是第一次挂载,否则就是更新
接下来瞅一眼 HooksDispatcherOnMount 和 HooksDispatcherOnUpdate
const HooksDispatcherOnMount: Dispatcher = {
readContext,
useCallback: mountCallback,
useContext: readContext,
useEffect: mountEffect,
useImperativeHandle: mountImperativeHandle,
useLayoutEffect: mountLayoutEffect,
useMemo: mountMemo,
useReducer: mountReducer,
useRef: mountRef,
useState: mountState,
useDebugValue: mountDebugValue
};
const HooksDispatcherOnUpdate: Dispatcher = {
readContext,
useCallback: updateCallback,
useContext: readContext,
useEffect: updateEffect,
useImperativeHandle: updateImperativeHandle,
useLayoutEffect: updateLayoutEffect,
useMemo: updateMemo,
useReducer: updateReducer,
useRef: updateRef,
useState: updateState,
useDebugValue: updateDebugValue
};
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
- 两个里面都有这些 hooks 的方法,虽然方法名一样,但是实现方式却完全不同
- 品,你细品
# 初始化阶段(mountState)
细品一下 mountState 方法
function mountState<S>(
initialState: (() => S) | S
): [S, Dispatch<BasicStateAction<S>>] {
// 访问Hook链表的下一个节点,获取到新的Hook对象
const hook = mountWorkInProgressHook();
// 获取初始化state
// useState 有两种传初始值的方式
// 一种是直接传值
// 一种是传入函数,最后返回值
// 这里判断如果是函数的话,会自动执行掉拿到返回值
if (typeof initialState === "function") {
initialState = initialState();
}
// 存入memoizedState,因为在mount还是在update的时候,update的时候
// 期望每次重新执行函数的时候,都能得到更新后的值
hook.memoizedState = hook.baseState = initialState;
// 初始化队列
const queue = (hook.queue = {
last: null,
dispatch: null,
lastRenderedReducer: basicStateReducer,
lastRenderedState: (initialState: any)
});
const dispatch: Dispatch<
BasicStateAction<S>
> = (queue.dispatch = (dispatchAction.bind(
null,
// Flow doesn't know this is non-null, but we do.
((currentlyRenderingFiber: any): Fiber),
queue
): any));
return [hook.memoizedState, dispatch];
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
- 获取初始化 state,将 state 存入
memoizedState进行保存 - 建立一个 update 队列
- 返回 memoizedState 和 dispatch
# 更改 state 的阶段
useState 抛出了变量和更改变量的方法,也就是我们上面看到的 dispatch
再来看看 dispatch 传入了啥
dispatchAction
const update: Update<S, A> = {
expirationTime,
action,
eagerReducer: null,
eagerState: null,
next: null
};
// Append the update to the end of the list.
const last = queue.last;
// 把当前创建的更新,放入队列的最后
if (last === null) {
// This is the first update. Create a circular list.
update.next = update;
} else {
// 这是一个环, last 的next指向的是first
// 这把更新添加到last的next, update的next又指向first, 重新形成一个环
const first = last.next;
if (first !== null) {
// Still circular.
update.next = first;
}
last.next = update;
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
- 更改 state 的值的时候其实就是执行了
dispatch,类似 redux 的原理 - 创建了一个更新,将当前创建的更新放入队列的最后
- last 会指向 first,总是会形成环方便查找
dispatch一个包含 x 值的action到队列
继续往下,是一个优化手段
if (
fiber.expirationTime === NoWork &&
(alternate === null || alternate.expirationTime === NoWork)
) {
const lastRenderedReducer = queue.lastRenderedReducer;
if (lastRenderedReducer !== null) {
let prevDispatcher;
try {
const currentState: S = (queue.lastRenderedState: any);
const eagerState = lastRenderedReducer(currentState, action);
update.eagerReducer = lastRenderedReducer;
// 一个优化手段
update.eagerState = eagerState;
if (is(eagerState, currentState)) {
return;
}
} catch (error) {
} finally {
}
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
- 通过一个 if 来判断
fiber.expirationTime是否处于空闲时间段 - 当不忙的时候就把下一次的 state 计算好保存好
- 可有可无,一个优化手段
最后
// 最后执行一个调度
scheduleWork(fiber, expirationTime);
1
2
2
- 最后执行了一下
scheduleWork,重新走调度流程
# 更新阶段
- 由于在更新阶段的最后执行了
scheduleWork,重新走了调度流程,所以又重新执行useState的过程 - 根据前面的判断进入了更新阶段
- 执行 updateState 方法,循环执行所有update上的 action,得到最新的 state,然后保存到 memorizedState,返回memorizedState
useState上挂的是updateState方法
function updateState<S>(
initialState: (() => S) | S
): [S, Dispatch<BasicStateAction<S>>] {
return updateReducer(basicStateReducer, (initialState: any));
}
1
2
3
4
5
2
3
4
5
updateState方法其实就是返回了updateReducer方法
再深入到updateReducer中去
const hook = updateWorkInProgressHook();
const queue = hook.queue;
1
2
2
- 首先获取到更新队列
renderPhaseUpdates.delete(queue);
let newState = hook.memoizedState;
let update = firstRenderPhaseUpdate;
do {
const action = update.action;
// 执行reducer,得到新的 state,新的state再参与计算
newState = reducer(newState, action);
// 继续
update = update.next;
} while (update !== null);
if (!is(newState, hook.memoizedState)) {
markWorkInProgressReceivedUpdate();
}
// 更新memoizedState的值
hook.memoizedState = newState;
if (hook.baseUpdate === queue.last) {
hook.baseState = newState;
}
queue.lastRenderedState = newState;
// 返回新值了
return [newState, dispatch];
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
- 继续往下,判断
numberOfReRenders > 0时开始渲染 - 获取到
memoizedState中保存的state - 进行一个do while 循环,循环里执行reducer去得到新的state
- 循环结束后得到最新的state,并更新
memoizedState的值
# 整体流程