# React 源码解读(三) requestWork
# requestWork
requestWork
function requestWork(root: FiberRoot, expirationTime: ExpirationTime) {
// 把root添加到调度队列, 链表的形式
addRootToSchedule(root, expirationTime);
// 在render过程当中, 直接返回return
// batchedUpdate 批处理 setState isRendering=true 第二个setState
// 不会出现频繁式的更新
if (isRendering) {
// Prevent reentrancy. Remaining work will be scheduled at the end of
// the currently rendering batch.
return;
}
if (isBatchingUpdates) {
// Flush work at the end of the batch.
// 执行unbatchedUpdates()时会设置为true
if (isUnbatchingUpdates) {
// ...unless we're inside unbatchedUpdates, in which case we should
// flush it now.
nextFlushedRoot = root;
nextFlushedExpirationTime = Sync;
// 立即执行更新
performWorkOnRoot(root, Sync, false);
}
// 批处理 return 不执行
return;
}
// TODO: Get rid of Sync and use current time?
// 同步任务,直接执行
if (expirationTime === Sync) {
// 立即同步执行
performSyncWork();
} else {
// 通过ExpirationTime 进行调度
scheduleCallbackWithExpirationTime(root, expirationTime);
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
requestWork 是 scheduleWork 中的一个重点 其中主要分成了三个分支:
- isRendering
- isBatchingUpdates
- expirationTime === Sync
我们来分别解释一下
1. isRendering
isRendering 顾名思义在render过程当中, 此时直接返回return。
batchedUpdate 批处理的时候,将 isRendering 置成 true,这样每次在执行 setState 时,都会走 isRendering 的分支直接返回,阻止更新,相当于暂停住,当第二个setState时依旧直接返回,避免出现频繁式的更新,也就是批处理。
2. isBatchingUpdates
isBatchingUpdates 中又有一个 isUnbatchingUpdates 分支。 isUnbatchingUpdates 会在执行 unbatchedUpdates() 时设置为true。 也就是在首次渲染的时候不需要进行批处理,所以就会进行立即更新。 这里的两个变量名可能会造成误解,isBatchingUpdates 和 isUnbatchingUpdates 这两个变量并不是互斥的,而是在两个方法中设置的哨兵变量。
如果是批处理的过程中的话,也会直接return。
3. expirationTime === Sync
当前面的 expirationTime 被设置成了同步任务的时候,就会立即执行。 剩余的则会进入 scheduleCallbackWithExpirationTime 通过ExpirationTime 进行调度。
# performWorkOnRoot
再继续从 requestWork 深入,执行了 performWorkOnRoot 方法
1. 首先进入先将 isRendering 置成true,告诉外面,现在要开始干活了,不要来打扰我
2. 判断是否是同步任务 if(!isYieldy)
进入分支后,判断是否存在任务了,如果 finishedWork 存在,就进行 commit,也就是 completeRoot() 如果没有任务,这个Root,之前有暂停的话,清除掉这个定时器,会尝试继续渲染。 之后会继续进行判断。
总结起来两句话:
通过是否存在 finishedWork 来判断是执行 commit 还是继续render
如果没有 finishedWork,执行 RenderRoot 后再判断是否执行 commit
// update队列
let finishedWork = root.finishedWork;
// 判断是否存在任务了
if (finishedWork !== null) {
// This root is already complete. We can commit it.
// 存在任务了
// finishedWork存在,进行commit了
completeRoot(root, finishedWork, expirationTime);
} else {
// root.finishedWork 有可能是其他什么值 undefined 之类的,重新置成 null 没毛病
root.finishedWork = null;
// If this root previously suspended, clear its existing timeout, since
// we're about to try rendering again.
// 如果这个Root,之前有暂停,清除掉这个定时器,会尝试继续渲染
const timeoutHandle = root.timeoutHandle;
if (timeoutHandle !== noTimeout) {
root.timeoutHandle = noTimeout;
// $FlowFixMe Complains noTimeout is not a TimeoutID, despite the check above
cancelTimeout(timeoutHandle);
}
// 继续调度
renderRoot(root, isYieldy);
finishedWork = root.finishedWork;
if (finishedWork !== null) {
// We've completed the root. Commit it.
// 判断是否可以执行commit
completeRoot(root, finishedWork, expirationTime);
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
3. 否则就是异步任务
跟同步的逻辑差不多
4. 最后任务结束再将 isRendering 置成false
# renderRoot
再来看一下 performWorkOnRoot 中继续调度时调用的 renderRoot()
其中下面这段代码是在hooks的时候用的
// 设置 ReactCurrentDispatcher, 包含所有hooks的实现
const previousDispatcher = ReactCurrentDispatcher.current;
ReactCurrentDispatcher.current = ContextOnlyDispatcher;
2
3
再往下,判断是否有新的更新进来
if (
expirationTime !== nextRenderExpirationTime ||
root !== nextRoot ||
nextUnitOfWork === null
)
2
3
4
5
进入 if 后
创建一个镜像Fiber,赋值给alternate属性。 WorkInProgress 是当前fiber对象的一个镜像,当再次进入时,Fiber发生了变化,直接与 WorkInProgress Fiber 对比。相当于缓存了之前更新的结果,并且放在了 Fiber.alternate 上面。同时将 Fiber 挂在 WorkInProgress Fiber上,进行了一个双缓存
// 重置
resetStack();
nextRoot = root;
nextRenderExpirationTime = expirationTime;
// 创建镜像Fiber, 赋值给alternate属性
// 是当前fiber对象的一个镜像,WorkInProgress Fiber对象
// Fiber发生了变化,直接与 WorkInProgress Fiber 对比
// Fiber.alternate = WorkInProgress Fiber
// WorkInProgress.alternate = Fiber
nextUnitOfWork = createWorkInProgress(
nextRoot.current,
null,
nextRenderExpirationTime,
);
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
中间的逻辑忽略,继续向下找。 从这里开始了 workLoop,下面是一个do while(true)的大循环。 接下来就要进入到 workLoop 中去了。
startWorkLoopTimer(nextUnitOfWork);
do {
try {
workLoop(isYieldy);
} catch (thrownValue) {
//......
}
break;
} while (true);
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
# workLoop
workLoop 中调用 performUnitOfWork,performUnitOfWork 中又调用了 beginWork workLoop => performUnitOfWork => beginWork 那我们直接来看 beginWork 的逻辑
首先判断节点是否存在,然后进行新旧props判断。
接下来用switch case 来判断不同的 workInProgress.tag 来进行入栈操作 beginWork
const updateExpirationTime = workInProgress.expirationTime;
// 判断节点是否存在
if (current !== null) {
const oldProps = current.memoizedProps;
const newProps = workInProgress.pendingProps;
// 前后props是否相等
// 判断了是否有老版本context使用并且发生变化
if (oldProps !== newProps || hasLegacyContextChanged()) {
// If props or context changed, mark the fiber as having performed work.
// This may be unset if the props are determined to be equal later (memo).
didReceiveUpdate = true;
// 需要更新的优先级小于当前更新的优先级
} else if (updateExpirationTime < renderExpirationTime) {
didReceiveUpdate = false;
// switch (workInProgress.tag) case
}
return bailoutOnAlreadyFinishedWork(
current,
workInProgress,
renderExpirationTime,
);
}
} else {
didReceiveUpdate = false;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
再接下来
// 在进入开始阶段之前,清除到期时间。
workInProgress.expirationTime = NoWork;
// 就根据不同的节点类型进行更新
// 真正在这个下面的逻辑里面打上标签EffectTag, 将 update 加入到 updateQuene 中,产生 finishWork
// update => updateQuene => finishWork
switch (workInProgress.tag) {}
// FunctionalComponent在第一次创建 Fiber 的时候就是 IndeterminateComponent
// 会调到 reconcileChildren 这个方法, 判断是否能够复用,执行节点的更新
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
在 ReactSideEffectTags 中定义了各种更新时的二进制表示法。这样在打 effectTag 的时候就直接进行位运算就可以得出要做什么操作。
ReactSideEffectTags.js
export const PerformedWork = /* */ 0b000000000001;
workInProgress.effectTag |= PerformedWork
# 总结
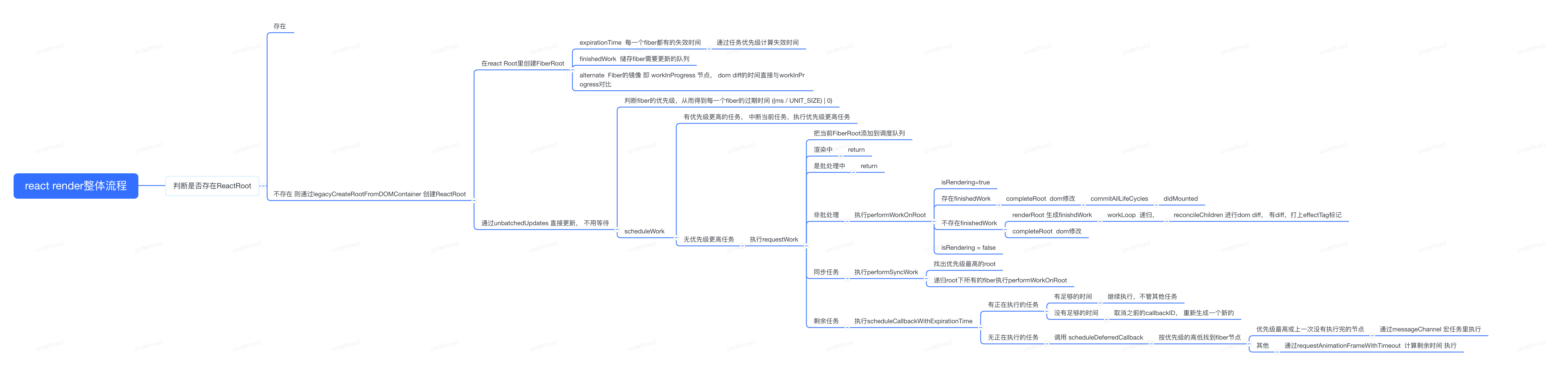
# performSyncWork
# scheduleCallbackWithExpirationTime
function scheduleCallbackWithExpirationTimescheduleCallbackWithExpirationTime(
root: FiberRoot,
expirationTime: ExpirationTime,
) {
// 判断是否还有正在跑的任务
if (callbackExpirationTime !== NoWork) {
// 判断任务优先级, 优先级低的任务直接return
if (expirationTime < callbackExpirationTime) {
// Existing callback has sufficient timeout. Exit.
return;
} else {
// 清空之前的callbackID
if (callbackID !== null) {
// 现有的回调没有足够的超时。 取消并安排一个新的。
cancelDeferredCallback(callbackID);
}
}
} else {
startRequestCallbackTimer();
}
// 设置新的callback和callbackExiporationTime
callbackExpirationTime = expirationTime;
const currentMs = now() - originalStartTimeMs;
const expirationTimeMs = expirationTimeToMs(expirationTime);
// 判断是否超时
const timeout = expirationTimeMs - currentMs;
// 生成一个 callbackID,用于关闭任务
// scheduledCallback = callback;
// 把callBack为performAsyncWork 赋给 scheduledCallback,
// scheduleDeferredCallback = unstable_scheduleCallback => requestHostCallback => requestAnimationFrame
callbackID = scheduleDeferredCallback(performAsyncWork, {timeout});
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32